# 13.2:@State
@State 装饰器是最基础的状态装饰器,它修饰的变量称为 状态变量,一旦 状态变量 的值发生了变化,那么用到该状态变量的组件会重新渲染从而实现 UI 刷新的功能。
# 13.2.1:约束与限制
@State 装饰器修饰的变量必须 指定类型 和 初始化
@State装饰器修饰的变量必须指定类型和初始化,否则编译报错:The @State property 'XXXX' must be specified a default value.
# 13.2.2:简单使用
@State 装饰器的使用很简单,直接在组件内的变量前添加 @State 即可。简单样例如下所示:
@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state {
message1: string = 'Hello World' // 变量 message1 没有@State装饰器
@State
message2: string = 'Hello World' // 变量 message2 添加@State装饰器
build() {
Column({space: 10}) {
Button(this.message1)
.fontSize(30)
.id("button1")
.onClick(() => {
this.message1 = "Hello, OpenHarmony";
})
Button(this.message2)
.fontSize(30)
.id("button2")
.onClick(() => {
this.message2 = "Hello, 《ArkUI实战》";
})
}
.padding(10)
.width('100%')
.height("100%")
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
简单样例运行结果如下所示:

上述样例中,属性 message1 和 message2 都赋值了默认值,只是 message2 添加了 @State 装饰器。分别点击 button1 和 button2 表现如下:
点击button1:
把 message1 被赋予了
Hello, OpenHarmony,此时页面无反应;点击button2:
把 message2 被赋予了
Hello, 《ArkUI实战》,此时页面显示新值。
结果按钮2的文字则显示了新值,由此可见是 @State 装饰器导致了按钮2发生了重绘。
📢:@State 装饰器修饰的变量必须 指定类型 和 初始化,否则编译报错:The @State property 'XXXX' must be specified a default value.
# 13.2.3:@State的作用域
@State 装饰器装饰的变量是私有的,只能在当前组件范围内访问,简单样例如下所示:
@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state {
message1: string = 'Hello World'
@State
message2: string = 'Hello World'
build() {
Column({space: 10}) {
Button(this.message1)
.fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.message1 = "Hello, 《ArkUI实战》";
})
Button(this.message2)
.fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.message2 = "Hello, 《ArkUI实战》";
})
CustomButton()
}
.padding(10)
.width('100%')
.height("100%")
}
}
@Component struct CustomButton {
@State
message2: string = 'Hello CustomWidget'
build() {
Button(this.message2)
.fontSize(30)
.onClick(() => {
this.message2 = "《ArkUI实战》, Hello";
})
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
样例运行结果如下图所示:
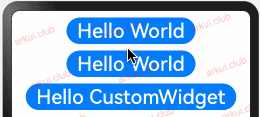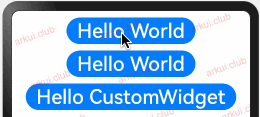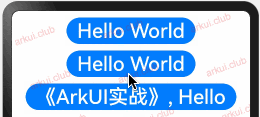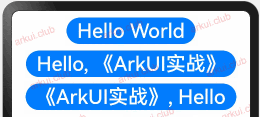
由运行结果可知,父子组件虽然都定义了状态变量,但是 CustomButton 内部的 message2 的值发生了更改但不会引发外部 Page_02_state 组件的状态变化。
# 13.2.4:@State支持的数据类型
@State 装饰器目前支持的数据类型主要如下:
简单数据类型
简单数据类型目前支持的类型有: number, boolean, string, enum。简单样例如下所示:
enum ColorType { R, G, B } @Entry @Component struct Page_02_state { @State message1: string = 'Hello World' // 定义 string 类型 @State message2: number = 10086 // 定义 number 类型 @State message3: boolean = false // 定义 boolean 类型 @State message4: ColorType = ColorType.R // 定义 enum 类型 build() { Column({space: 10}) { Button(this.message1) .fontSize(30) .onClick(() => { this.message1 = "Hello, 《ArkUI实战》"; }) Button(this.message2.toString()) .fontSize(30) .onClick(() => { this.message2 = 10010 }) Button(this.message3.toString()) .fontSize(30) .onClick(() => { this.message3 = true }) Button(this.message4.toString()) .fontSize(30) .onClick(() => { this.message4 = ColorType.B }) } .padding(10) .width('100%') .height("100%") } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41样例运行结果如下图所示:
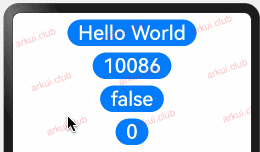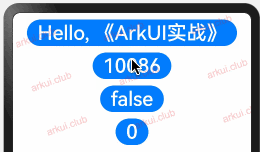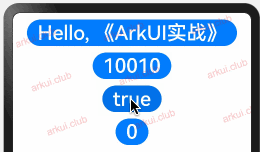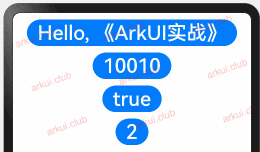
简单数组类型
简单数据类型 目前支持的有: number, boolean, string, enum,笔者把由它们组成的 数组 简称为简单数组,目前简单数组支持的操作为:数组重新赋值,数组单项赋值,数组数据添加 和 数组数据删除,以上支持的操作会引起相关组件的重绘。简单样例如下所示:
@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state { @State message2: number[] = [] build() { Column({space: 10}) { Text("message2 total: " + this.total()) .fontSize(20) Button("添加操作") .onClick(() => { this.message2.push(Math.round(Math.random() * 100)) // 数组添加数据操作 }) Button("删除操作") .onClick(() => { this.message2.pop() // 数组删除数据操作 }) Button("重新赋值") .onClick(() => { this.message2 = [100, 200, 300] // 数组重新初始化 }) Button("单项赋值") .onClick(() => { this.message2[0] = 500 // 数组单项数据更新 }) } .padding(10) .width('100%') .height("100%") } // 计算数组总和 private total(): number { let total = 0 this.message2.forEach((value: number) => { total += value }) return total } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40样例运行结果如下图所示:

class、Object 类型
当装饰的数据类型为 class 或 Object 时,支持的操作为:自身赋值 和 自身属性赋值 操作,也就是 Object.keys(observedObject) 返回的所有属性的赋值操作,简单样例如下所示:
class Headmaster { public name: string; constructor(name: string) { this.name = name; } } class Student { public name: string; constructor(name: string) { this.name = name; } } class Teacher { public headmaster: Headmaster; public students: Student[]; public name: string; public age: number; constructor(headmaster: Headmaster, student: Student[], name: string, age: number) { this.headmaster = headmaster; this.students = student; this.name = name; this.age = age; } } @Entry @Component struct Page_02_state { headmaster: Headmaster = new Headmaster("刘校长"); student: Student = new Student("张三"); @State teacher: Teacher = new Teacher(this.headmaster, [this.student], "张老师", 26); build() { Column({space: 10}) { Text("老师姓名: " + this.teacher.name + "\n老师年龄:" + this.teacher.age + "\n老师领导:" + this.teacher.headmaster.name + "\n教有学生:" + this.teacher.students.length + "\n学生名字:" + this.studentNames()) .fontSize(20) Button("重新赋值") .onClick(() => { this.teacher = new Teacher(new Headmaster("王校长"), [this.student], "王老师", 30); }) Button("属性赋值") .onClick(() => { this.teacher.students = [new Student("李四"), new Student("王五")]; this.teacher.age = 40; this.teacher.name = "新来的刘老师" this.teacher.headmaster = new Headmaster("新来的吕校长") }) Button("嵌套赋值") .onClick(() => { this.teacher.headmaster.name = "新来的刘校长" this.teacher.students.push(new Student("新来的王同学")) this.teacher.students[0].name = "新来的刘同学"; this.teacher.students.pop() }) } .padding(10) .width('100%') .height("100%") } private studentNames(): string { let names = ""; this.teacher.students.forEach((student) => { names = names.concat(student.name).concat(","); }); return names; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70样例运行结果如下图所示:

由样例运行结果可知,@State 装饰器修饰的 class 或者 object,支持自身的 重新初始化 和 自身属性 的重新赋值操作。
# 13.2.5:@State初始化顺序
@State 装饰器装饰的状态数据初始化顺序可以归纳为:本地初始化、由父组件来初始化,父组件给子组件初始化,简图如下所示:
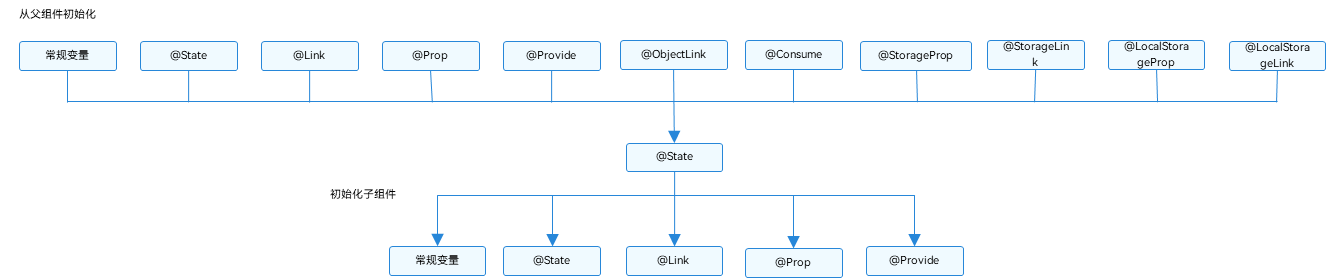
自身的本地初始化:
本地初始化比较好理解,就是在定义状态数据的时候直接赋予初始值,样例代码如下:@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state { @State count: number = Math.random(); // 定义count时直接赋予初始值 build() { Column({space: 10}) { Text("count: " + this.count) .fontSize(22) .onClick(() => { this.count = Math.random(); }) } .padding(10) .width("100%") .height("100%") } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17样例运行结果如下图所示:

由父组件来初始化:
由父组件来初始化指的是 @State 装饰的状态变量可以由父组件传值来初始化,此时父组件传递进来的值会覆盖本地的数据。简单样例如下所示:@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state { @State count1: number = 10086; count2: number = 10010; build() { Column({space: 10}) { Text("父组件count: " + this.count1) .fontSize(22) .onClick(() => { this.count1 = Math.round(Math.random() * 1000); this.count2 = this.count1; }) CustomText({count: this.count1}) CustomText({count: this.count2}) } .padding(10) .width("100%") .height("100%") } } @Component struct CustomText { @State count: number = -1 build() { Text("子组件count: " + this.count) .fontSize(22) .onClick(() => { this.count = Math.round(Math.random() * 1000); }) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37样例运行结果如下图所示:
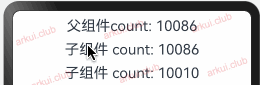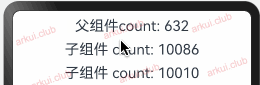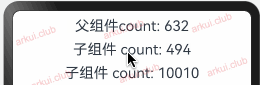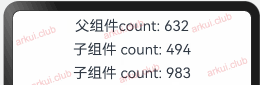
由上图运行结果可知,子组件
CustomText里虽然定义了状态变量并赋予了初始值,但在父组件中使用时给其传递了新值,此时新值会覆盖子组件中的初始值。向子组件去初始化:
向子组件去初始化指的是 @State 装饰的状态变量可以由父组件向子组件传值来初始化,此时父组件传递进来的值会覆盖子组件本地的初始值。简单样例如下所示:@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state { build() { Column() { CustomLayout() } .padding(10) .width("100%") .height("100%") } } @Component struct CustomLayout { @State count3: number = 3; count4: number = 4; build() { Column({space: 10}) { CustomText1({ count5: this.count4, count6: this.count3 }) } .width("100%") .height("100%") } } @Component struct CustomText1 { @State count5: number = 5; count6: number = 6; build() { Column() { Text("count5: " + this.count5) .fontSize(22) .onClick(() => { this.count5 = Math.round(Math.random() * 1000); this.count6 = this.count5 }) Text("count6: " + this.count6) .fontSize(22) .onClick(() => { this.count6 = Math.round(Math.random() * 1000); }) } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53样例运行结果如下图所示:
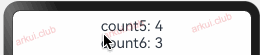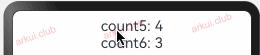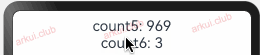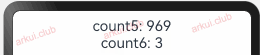
由上述样例可知,子组件
CustomText1中的 count5 和 count6 赋予了默认值,在父组件中使用的时候把默认值覆盖了。
# 13.2.6:完整样例
笔者结合 List 组件实现一个 添加,删除,重置 和 局部更新 的小样例,代码如下所示:
class Student {
public name: string;
public age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
@Entry @Component struct Page_02_state {
@State students: Array<Student> = [];
build() {
Column({space: 10}) {
List({
space: 10
}) {
ForEach(this.students, (item: Student, index: number) => {
ListItem() {
Row() {
Text(index.toString())
.width(50)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Column() {
Text(item.name + index)
.fontSize(18)
Text("age: " + item.age)
.fontSize(12)
}
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start)
.layoutWeight(1)
.height("100%")
}
.borderRadius(10)
.backgroundColor("#aabbcc")
.width("100%")
.height(45)
}
.width("100%")
.height(45)
})
}
.width("100%")
.layoutWeight(1)
Row({space: 5}) {
Button("添加")
.onClick(() => {
this.students.push(new Student("张三", Math.round(Math.random() * 100 + 1)));
})
Button("删除")
.onClick(() => {
this.students.pop();
})
Button("重置")
.onClick(() => {
this.students = [];
})
Button("更新 1")
.onClick(() => {
this.students[this.students.length - 1] = new Student("新来的张三", 20);
})
Button("更新 2")
.onClick(() => {
this.students[this.students.length - 1].age = 110;
this.students[this.students.length - 1].name = "新来的学生"
})
}
.width("100%")
}
.padding(10)
.width('100%')
.height("100%")
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
样例运行结果如下图所示:

← 13.1:前言 13.3:@Prop →

